Experiential travel focuses on creating meaningful, immersive, and personalised travel experiences beyond traditional sightseeing. It emphasises engaging with local cultures, traditions, and environments to foster deeper connections with a destination. Travellers seek authenticity by participating in activities like cooking local dishes, attending cultural festivals, exploring off-the-beaten-path locations, or engaging with local communities. Experiential travel often prioritizes sustainability, cultural respect, and personal enrichment, catering to travellers who value storytelling, emotional impact, and transformative experiences over conventional tourism.
Experiential Travel – Table of Contents
History and Evolution of Experiential Travel
The Origins of Experiential Travel
Experiential travel is not a new phenomenon; the basis of almost all travel is experiences. Niche travel operators have packaged adventure activities alongside lodging for several decades, and the ‘Grand Tour’ of Europe made by Northern European and then American aristocrats 350 to 150 years ago was essentially a highly lavish version of experiential travel. Since the 1970s, printed guidebooks such as Frommers, Lonely Planet, and the Rough Guides have coupled local experiences with logistics, including hotel and restaurant listings, as have the monthly ‘What’s On’ format city magazines. However, even with the advent of the internet, they generally remained print/ebook guides, paid apps, or OTAs’ portals, reflecting available choices rather than marketing platforms.
The recent revolution in experiential travel, underpinned by low-cost travel and online/mobile technology, stems mainly from the extension of review sites and diversification of OTAs. Advances in payment systems and booking platforms developed by specialist providers and OTAs have created the ease and trust by which ‘experience providers’ can now transact globally. These platforms deliver real-time marketing channels, leveraging existing experience providers’ reach, actively inducing small start-up businesses to provide experiences, and rapidly expanding the market supply and choice.
Single-day and Multiday Experiences
Single-day experiences without lodging are the main supply growth segment. Such experiences previously would have been a potential motivation for travel, but were secondary to the hotel and overall destination. They would have been booked via the hotel concierge, a local tourist information desk, or directly on an individual experience website. Today, they form the core activity of distributors such as Viator and Airbnb Experiences.
Immersive multiday experiences are the mainstay of highly specialised/adventure tour operators. They generally require a high degree of logistics and coordination, are limited to small guest numbers, require management of delicate relationships, can be exposed to late changes, such as weather-related changes, and, especially in the case of rugged adventures, are subject to strict safety and high liability risks. The demand in this segment is undoubtedly on the rise, though, until the launch of Airbnb Adventures in June 2019, it remained the domain of adventure tour operators such as G Adventures and Audley Travel, except for a handful of select platforms, such as the arts-focused VAWAA.
The Future of Experiential Travel
These experiential travel platforms have opened long-tail tourism, allowing guests to pursue and indulge in specific, individual tastes, creating opportunities, driving competition, and changing hospitality distribution. Future technology, specifically AI, will probably further facilitate and fuel these trends. According to the ‘Megatrend: Experience More’ report from Euromonitor International, the experience economy, driven primarily by millennial consumers, should increase from $5.8 trillion in 2016 to $8 trillion in 2030, considering leisure, recreation, travel and food services.
Defining Experiential Travel
Experiential travel is a philosophy of gaining knowledge and building cultural capital that should lead to self-improvement and self-care. What is and isn’t experiential travel is disputed. However, it should not provide a simple service, such as A-to-B transportation, something someone can easily accomplish on their own, like purchasing a meal or entering a public museum, nor should it be a crowded, impersonal tour.
The General Principles of Experiential Travel
General principles of experiential travel are that they should fulfil most if not all of the following criteria:
| Principle | Aim |
|---|---|
| Active | Allows individuals to explore their passions, values, and identity through unique and fulfilling active experiences. |
| Aesthetic | Enriches the spirit by engaging with the beauty of art, landscapes, and cultural expressions. |
| Authentic | Prioritise genuine, unfiltered experiences that reflect the true culture, history, and lifestyle of a destination. |
| Discovery | Satisfies the innate need for exploration, learning, and discovering the unknown. |
| Immersive | Encourage active participation in local traditions, crafts, food, or daily life rather than passive observation. |
| Local | Emphasise interactions with locals to build personal relationships and gain deeper insights into their lives. |
| Meaningful | Provides a sense of purpose by engaging in activities that feel significant and impactful. |
| Mindfulness | It encourages living in the moment and appreciating the beauty of the here and now. |
| Personal | Design travel experiences tailored to individual interests, preferences, and goals. |
| Responsible | Nurtures a sense of stewardship for the world by promoting sustainable and ethical travel practices. |
| Storytelling | Focus on creating unique narratives and memorable moments for travellers to cherish and share. |
| Sustainable | Promote eco-friendly practices, responsible tourism, and respect for the environment and local communities. |
| Transformative | Aim to leave a positive impression on the traveller, encouraging personal growth, self-discovery, or a new perspective on life. |
Types of Experiential Travel
Examples of travel experiences can be highly varied and cross several themes, such as adventure tours that combine elements of nature and food. They can be as simple as a one-hour walk with an informative local guide along a nature trail, an exhilarating four-day mountain trek, or a twelve-week worldwide ballooning adventure.
Cultural Travel
Cultural travel allows travellers to deeply connect with a destination’s heritage, traditions, and daily life. It can involve activities such as guided city walks that reveal historical and architectural treasures, attending vibrant local festivals and music performances, or participating in ceremonies that showcase unique customs.
Travellers may engage in homestays or local living experiences to gain an authentic perspective on community life, learn traditional crafts, arts, or languages, and participate in rituals that embody a culture’s identity. Cultural travel can also extend to community-based tourism, where visitors contribute to local development projects, such as building schools, mentoring, or sharing skills, fostering mutual understanding and meaningful exchanges. These experiences allow travellers to move beyond being mere spectators, becoming active participants in the cultural fabric of the places they visit.
Educational Travel
Educational travel combines the excitement of exploration with the opportunity to gain new skills and knowledge, creating enriching and transformative experiences. Through hands-on workshops and immersive courses, it encompasses activities such as learning art, photography, pottery, dance, yoga, sailing, creative writing, or a new language. Travellers can participate in specialised programs led by experts, attend retreats focused on personal growth, or engage in academic travel into history, science, or cultural studies. Cultural exchange programs further enhance the experience by fostering cross-cultural understanding and collaboration.
Culinary Travel
Culinary travel is a journey that connects travellers with the essence of a destination through its food and drink, offering a sensory exploration of culture, history, and traditions. This experiential travel delves into the entire food journey, from sourcing and production to cooking, tasting, and storytelling.
Travellers engage in immersive activities such as guided food and wine tours, cooking classes with local chefs, or visits to farms, vineyards, and distilleries to learn about the origins and craftsmanship behind regional cuisine. Culinary experiences may include participating in harvest festivals, touring bustling local markets, or foraging with knowledgeable locals for wild ingredients. Travellers can enjoy farm-to-table dining, where they witness the journey of ingredients from field to plate or savour home-cooked meals shared with families.
Nature & Agrotourism Travel
Nature and agritourism travel immerse travellers in the beauty of the natural world and rural life, fostering a deeper appreciation for the environment and sustainable living. Nature travel may include leisurely activities such as country walks, visits to national parks, conservation areas, and animal sanctuaries, as well as birdwatching, camping, fishing, hunting, or wildlife photography. For those seeking more active engagement, it can involve participating in environmental restoration or conservation projects, helping protect ecosystems and wildlife. Agritourism offers hands-on experiences, such as staying on a working farm, harvesting crops, learning traditional farming techniques, or exploring vineyards, olive groves, and tea or coffee plantations.
Festival & Event-Based Travel
Festival- and event-based travel offers a vibrant, dynamic way to experience a destination’s energy, traditions, and communal spirit. It encompasses attending cultural celebrations like Carnival or Oktoberfest, immersing in the creativity of art and music festivals, or enjoying live concerts that showcase local talent and global stars. Seasonal festivals and harvest celebrations provide a window into the traditions tied to a region’s heritage. This type of travel for sports enthusiasts includes attending world-class events such as the Olympics, major football tournaments, or iconic marathons as a spectator or participant.
Historical & Archaeological Travel
Historical and archaeological travel allows travellers to step back in time and connect with the stories and legacies of ancient civilisations. It may involve exploring ancient ruins, iconic UNESCO World Heritage Sites, or historically rich cities that bring history to life through their architecture and culture. Travellers can deepen their engagement by participating in archaeological digs or workshops, uncovering artefacts, and gaining hands-on insight into the techniques used to piece together the past. Reenactments and living history experiences add an interactive dimension, immersing visitors in the customs, traditions, and daily lives of bygone eras.
Religious & Pilgrimage Travel
Religious and pilgrimage travel is one of the oldest and most inherently experiential forms of tourism, centred on immersion, reflection, ritual, and personal transformation rather than passive observation. Unlike conventional heritage visits, experiential religious travel involves structured journeys with narrative progression, participation in ceremonies or spiritual practices, engagement with sacred texts in context, and interaction with faith communities.
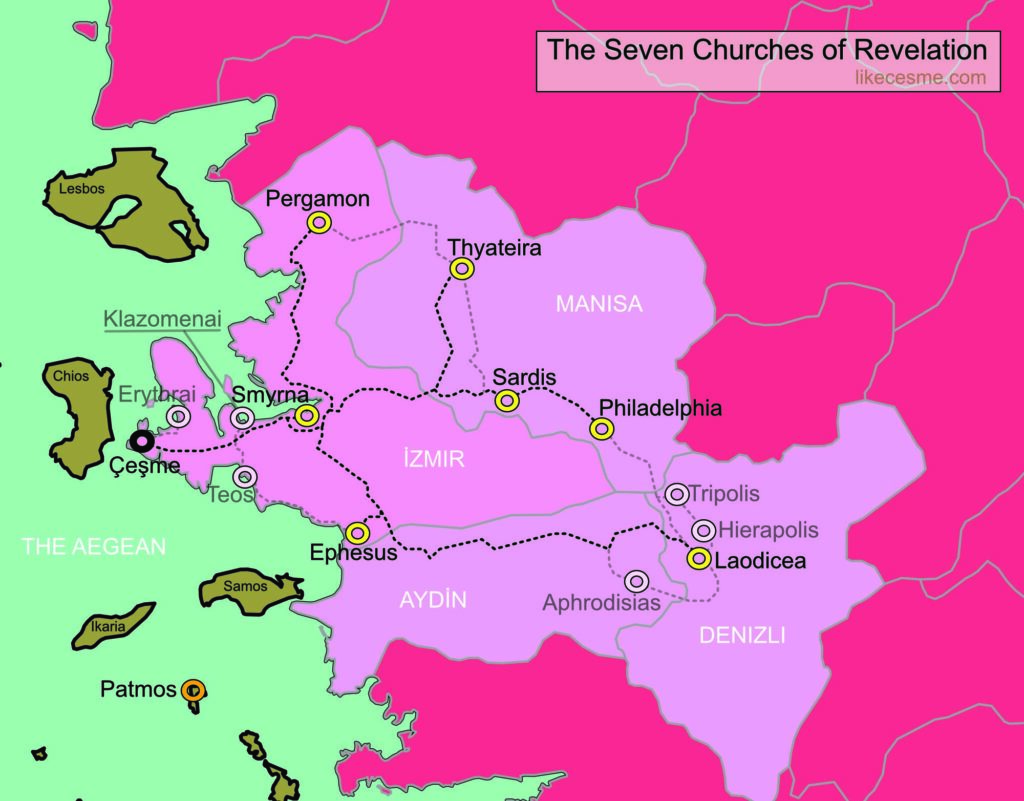
A strong example is the tour of the Seven Churches of Revelation in western Anatolia, where scripture, archaeology and landscape combine to create a multi-day reflective journey rather than a simple site tour. Comparable experiential religious travel includes walking the Camino de Santiago, undertaking the Hajj pilgrimage, visiting Varanasi for Hindu rituals, or participating in monastery stays and spiritual retreats, all of which align with the principles of authenticity, immersion, meaning, and transformation that define experiential travel.
Soft Adventure Travel
Soft adventure experiential travel involves low-risk, accessible activities that offer adventure without requiring advanced skills or intense physical effort. These experiences focus on enjoyment, connection with nature, and cultural immersion, often catering to travellers of all ages and fitness levels. Examples include hiking, cycling, skiing, or horse riding on well-maintained trails; wildlife safaris; sailing or kayaking on calm waters; hot air balloon rides; shallow-water scuba diving; or guided cultural tours in remote regions. The emphasis is on comfort, safety, and discovering a destination’s beauty and heritage in a relaxed and engaging manner. Soft adventure allows travellers to escape their routine while maintaining a sense of ease and security.
Hard Adventure Travel
Hard adventure experiential travel is more physically demanding and often involves greater risk, requiring specialised skills, equipment, or training. It appeals to thrill-seekers and experienced adventurers looking for challenging, adrenaline-fueled experiences. This category includes mountaineering, deep-sea/shark diving, white-water rafting, skydiving, bungee jumping, extreme trekking in remote wilderness, caving and ice climbing. It often takes travellers to isolated or rugged locations, fostering a more profound sense of accomplishment, resilience, and connection with the natural world. While safety remains a priority, these experiences push participants beyond their comfort zones, offering a more intense and transformative form of experiential travel.
Experiential Travel Distribution Platforms
Global distribution platforms for independent experience providers and localised tour companies that established themselves over the past decade include:
Viator (TripAdvisor Experiences): Founded in 2016 Viator is a TripAdvisor company and the market leader in tour and activity listings, and lists 200,000 tours, activities, attractions and experiences around the world. Viator is optimised for mobile booking and features 24-hour cancellation policy, lowest price guarantee, millions of customer reviews, and 24/7 multilingual customer care.
Get Your Guide: Since the platform’s foundation in 2009, they have booked more than 25 million tours, activities, and attraction tickets. A global team of over 500 travel experts and technologists, the company is headquartered in Berlin, Germany and has offices in 14 countries worldwide. In May 2019, Get Your Guide raised $484 million in series E financing led by the SoftBank Vision Fund to broaden inventory, increase the capabilities of the platform – enhance the booking experience, and expand and diversify its marketing channels
Expedia Local Expert: Launched in 2014 it is part of Expedia Group, which operates the well-known Expedia travel booking platform. Expedia offers experience providers international exposure through global affiliate partner sites, including 69 unique websites and 17 languages. Expedia Local Expert operates concierge and activity desks in hotels and retail locations, a one-stop resource with local activities, tours, and transportation in over 750 vacation destinations allows the compilation of an activity itinerary.
Airbnb Experiences: Launched in November 2016, Airbnb’s single-day experience listings have increased within 24 months from 500 to 30,000 in over 1,000 cities, with year-on-year demand growing 700% in 2018. In the first two years, Airbnb learnt about the kind of experiences travellers are looking for and as a result, has given extra focus and resources to the food & drink and animal-related activities. Airbnb has promised aggressive investment, increased diversity, and a greater supply of experiences.
Airbnb Adventures: Launched in June 2019, Airbnb’s multiday adventure trips are all over 2-days and include curated itineraries, organised logistics, lodging and meals. The off-the-beaten-track immersive adventures are capped for a maximum of 12 persons and average $588 per person for a 3-day trip. Small local operators with specialist knowledge of each activity and destination organise the tours. They must go through a best practices and safety vetting process with Airbnb, as advised by the Adventure Travel Trade Association (ATTA).
VAWAA – Vacation with an Artist: Launched in November 2015 VAWAA is a platform providing the experience of short-term apprenticeships with 63 artists, designers, and creatives in 23 countries. The experience is for between 3-10 days, and guests who require no prior experience get approximately 4 hours per day of studio time with artists.
The experiences range from $300 to $3,000 per person, including artist fees, studio access, tools, materials, and VAWAA travel coordination, but typically exclude accommodation, meals, and travel expenses (a few artists do offer the opportunity to live in). Studio sessions are limited to 4 guests to respect the master’s space and preserve the intimate nature of the learning experience. Most artists speak English, and guests may take home their creative works.
Other experiential travel organisers include Fat Tire Tours which operates bicycle, segway and walking tours in 12 major cities. Peek a San Fransico based start-up founded in 2012 and 2018 announced a tie-up with Google to add its inventory to Google Search, Google Maps and Google Trips. Hong Kong-based Klook was founded in 2014 a travel activities, and services booking platform with 80,000 offerings in more than 250 destinations, and Taiwan-based KKday founded in 2014 that describes itself as the leading e-commerce travel platform that connects travellers with authentic local tours & activities.
Listings for the number of experiences and other data as published by respective websites as of June 2019
Hosting Commercial Experiences
These new distribution channels have also actively encouraged small entrepreneurial ventures. Below are some of the main sites host registration details, links and procedures:
Viator Experience Hosting: The Viator platform lists hosts on TripAdvisor Experiences, which lists 140,000 suppliers’ products on TripAdvisor’s ‘Things to do’ pages, the TripAdvisor App, at Viator.com, and through partners and affiliates. The TripAdvisor platform boasts over 600 million reviews and 455 million visitors monthly. Signing up as a supplier and listing experiences is free; guests pay in advance through the platforms. Viator retains a percentage of each booking, paying the balance after the commission is deducted from the provider.
Expedia Experience Hosting: Expedia works on a commission level agreed upon with a destination manager before site loading. Rates provided to Expedia must include taxes and charges. Expedia requires a banking form via DocuSign, a contact information form, a current certificate of liability insurance, descriptions of the product(s), eight high-definition images, and retail product rates. In addition to distribution, Expedia provides email marketing via newsletters and targeted emails, airline/hotel cross-selling, and search engine marketing.
Airbnb Experience Hosting: There is no prerequisite to be a property host, to host experiences, the criteria is a passion, unique perspective, an immersive/participative activity or access to an exclusive place/community. Airbnb offers a step-by-step guide to setting up hosting: (1) Learn quality standards, (2) create an experience page, and after the experience has been quality checked, (3) add availability and start the business. Fees are 20% commission for payment processing, customer services, and liability insurance (to $1 million, limited by activity risks), and Airbnb waives commissions for social impact experiences. The Airbnb interface provides guidance on tasks, payment, scheduling, and performance insights. Airbnb has stated that the average annual income per host in 2018 was $3,500.
Listings for the number of experiences and other data as published by respective websites as of June 2019
Further resources:
See Forbes Magazine (March 2025) – “Experiential Travel Is The New Mercedes-Benz“
